文章目录
-
- 执行流程
-
-
- 1,AOP拦截器入口
- 2,TransactionInterceptor
-
- 事物的核心处理
- 一,获取事物
-
- 1,`doGetTransaction()`获取当前事物
- 2,如果当前已存在事物
- 3,如果当前事物不存在
- 二,挂起事物
- 三,恢复事物
- 四,执行目标方法
- 五,异常回滚
- 六,事物提交
- 七,总结
执行流程
1,AOP拦截器入口
测试类:
public class TransactionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TransactionConfig.class);
BookService bean = applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class);
// 调用目标方法
bean.checkout("小明",1);
}
}
bean是代理类,bean.checkout("小明",1);会调到代理类中,然后回调到DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept()方法:
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
// 省略部分代码...
try {
// 从advised中获取配置好的AOP通知
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// 如果没有aop通知配置,那么直接调用target对象的调用方法
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
// 如果拦截器链为空则直接激活原方法
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// 通过cglibMethodInvocation来启动advice通知
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
}
}
这里分为两步:
1、 从Advisor中获取事物拦截器(TransactionInterceptor)或方法拦截器(MethodInterceptor);
2、 执行具体的拦截器链;
会调用到ReflectiveMethodInvocation类,是AOP拦截(执行拦截器链)的入口类:
// AOP拦截的执行入口类
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// 从索引为-1的拦截器开始调用,并按序递增,如果拦截器链中的拦截器迭代调用完毕,开始调用target的函数,这个函数是通过反射机制完成的
// 具体实现在AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection方法中
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// 获取下一个要执行的拦截器,沿着定义好的interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice链进行处理
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// 这里对拦截器进行动态匹配的判断,这里是对pointcut触发进行匹配的地方,如果和定义的pointcut匹配,那么这个advice将会得到执行
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// 如果不匹配,那么proceed会被递归调用,直到所有的拦截器都被运行过位置
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// 普通拦截器,直接调用拦截器,将this作为参数传递以保证当前实例中调用链的执行
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
}
上述方法是AOP拦截器的入口类,会遍历拦截器链中的所有拦截器,按事先排好序的顺序一个个执行。直到所有的拦截器都执行完成,再通过反射来执行目标方法:
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
// this.target 目标对象
// this.method 目标方法
// this.arguments 目标方法参数信息
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments);
}
目前事物拦截器只有一个TransactionInterceptor
2,TransactionInterceptor
TransactionInterceptor使用通用的spring事务基础架构实现“声明式事务”,继承自TransactionAspectSupport类(该类包含与Spring的底层事务API的集成),实现了MethodInterceptor接口。类图如下:
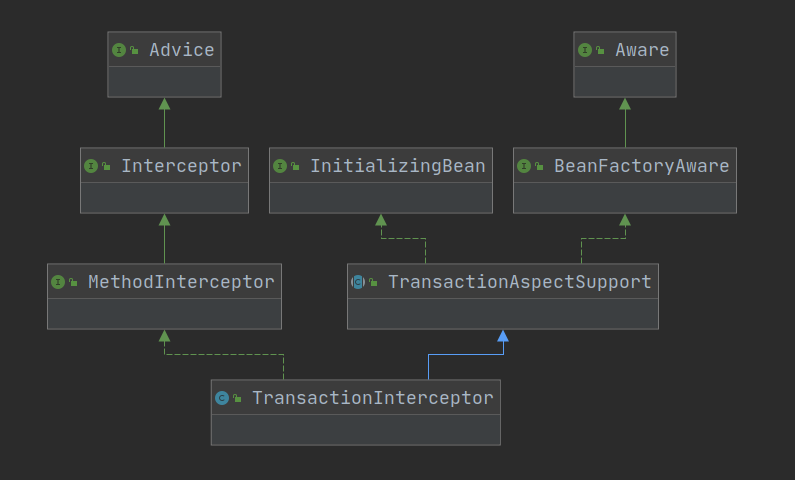
事务拦截器的拦截功能就是依靠实现了MethodInterceptor接口,这个是spring的方法拦截器,主要看invoke方法:
/**
* 事务拦截器,实现了方法拦截器MethodInterceptor
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取我们的代理对象的class属性
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
/**
* 以事务的方式调用目标方法
* 在这埋了一个钩子函数 用来回调目标方法的
*/
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
}
如上图TransactionInterceptor复写MethodInterceptor接口的invoke方法,并在invoke方法中调用了父类TransactionAspectSupport的invokeWithinTransaction()方法完成事物的核心处理。
其中,这里传了一个钩子方法(回调方法),用于回到我们AOP拦截处理入口,用于调用我们目标方法invokeJoinpoint()上面提到过!
接下来我们来看事物处理的核心方法TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction()
事物的核心处理
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取我们的事务属性源对象
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 通过事务属性源对象获取到当前方法的事务属性信息
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取我们配置的事务管理器对象
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 省略部分异常判断....
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
// 获取连接点的唯一标识 类名+方法名
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 声明式事务处理
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// 创建TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// 执行被增强方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
//清除事务信息,恢复线程私有的老的事务信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
//成功后提交,会进行资源储量,连接释放,恢复挂起事务等操作
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
// 省略编程式事物逻辑...
else{
}
// 省略部分代码...
return result;
}
}
}
上面主要完成如下流程:
1、 createTransactionIfNecessary():如果有必要,创建事务;
2、 invocation.proceedWithInvocation()执行目标方法;
3、 completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo,ex)异常回滚事物;
4、 commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo)提交事物;
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
// 获取TransactionStatus事务
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
}
// 根据指定的属性与status准备一个TransactionInfo,
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
上面分为两步:
1、 获取事物TransactionStatus;
2、 把获取到的事物TransactionStatus包装成prepareTransactionInfo;
一,获取事物
public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager, Serializable {
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// 如果没有事务定义信息则使用默认的事务管理器定义信息
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 获取事务
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 判断当前线程是否存在事务,判断依据为当前线程记录的连接不为空且连接中的transactionActive属性不为空
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// 当前线程已经存在事务
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// 事务超时设置验证
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// 如果当前线程不存在事务,但是PropagationBehavior却被声明为PROPAGATION_MANDATORY抛出异常
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,PROPAGATION_NESTED都需要新建事务
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
//没有当前事务的话,REQUIRED,REQUIRES_NEW,NESTED挂起的是空事务,然后创建一个新事务
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// 恢复挂起的事务
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// 创建一个空的事务
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
}
1,doGetTransaction()获取当前事物
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
// 创建一个数据源事务对象
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
// 是否允许当前事务设置保持点
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
/**
* TransactionSynchronizationManager 事务同步管理器对象(该类中都是局部线程变量)
* 用来保存当前事务的信息,我们第一次从这里去线程变量中获取 事务连接持有器对象 通过数据源为key去获取
* 由于第一次进来开始事务 我们的事务同步管理器中没有被存放.所以此时获取出来的conHolder为null
*/
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
// 非新创建连接则写false
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
// 返回事务对象
return txObject;
}
首先获取到当前 JDBC DataSource (jdbc数据源)然后调用TransactionSynchronizationManager 事务同步管理器对象获取当前线程且当前 JDBC DataSource 所对应的事物。
public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(TransactionSynchronizationManager.class);
// 线程私有事务资源
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
// 事务同步
private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transaction synchronizations");
// 当前事务的名称
private static final ThreadLocal<String> currentTransactionName =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction name");
// 当前事务是否只读
private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> currentTransactionReadOnly =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction read-only status");
// 当前事务的隔离级别
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> currentTransactionIsolationLevel =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction isolation level");
// 实际事务是否激活
private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> actualTransactionActive =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Actual transaction active");
@Nullable
public static Object getResource(Object key) {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Object value = doGetResource(actualKey);
if (value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Retrieved value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
return value;
}
@Nullable
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
Object value = map.get(actualKey);
// Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
value = null;
}
return value;
}
如果当我们第一次从这里去线程变量resources中获取 事务连接持有器对象 通过数据源为key去获取,由于第一次进来开始事务 我们的事务同步管理器中没有被存放.所以此时获取出来的conHolder为null。
如果当前线程不是第一次进来,则可以取到对应的事物持有器对象conHolder。
2,如果当前已存在事物
如果上面取到的事物持有器对象conHolder!=null,并且当前事物是活跃的,则证明当前已存在事物
则处理已存在事物:
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException {
/**
* 判断当前的事务行为是不是PROPAGATION_NEVER的
* 表示为不支持事务,但是当前又存在一个事务,所以抛出异常
*/
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
}
/**
* 判断当前的事务属性不支持事务,PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED,所以需要先挂起已经存在的事务
*/
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
}
// 挂起当前事务
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
// 创建一个新的非事务状态(保存了上一个存在事务状态的属性)
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
/**
* 当前的事务属性状态是PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW表示需要新开启一个事务状态
*/
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
}
// 挂起当前事务并返回挂起的资源持有器
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try {
// 创建一个新的非事务状态(保存了上一个存在事务状态的属性)
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) {
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
}
}
// 嵌套事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
// 不允许就报异常
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
// 嵌套事务的处理
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
// Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction,
// through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus.
// Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
// 如果没有可以使用保存点的方式控制事务回滚,那么在嵌入式事务的建立初始简历保存点
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
// 为事务设置一个回退点
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
else {
// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls.
// Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here
// in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction.
// 有些情况是不能使用保存点操作
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
// Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
}
if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
}
}
if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
}
}
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
如果当前已存在事物:
1、 如果当前事物传播特性是NEVER,表示为不支持事务,但是当前又存在一个事务,所以抛出异常;
2、 如果当前事物传播特性是NOT_SUPPORTED,表示不运行在事物中,则需要先挂起已经存在的事务,创建一个非事物状态(将当前事务对象设置为null,newTransaction设置为false);
3、 如果当前事物传播特性是REQUIRES_NEW,表示需要新开启一个事务状态,则需要挂起已经存在的事物,并开启一个新的事物;
4、 如果当前事物传播特性是NESTED,表示嵌套事物,则需要创建一个SAVEPOINT;
5、 如果当前事物传播特性是REQUIRED,SUPPORT,MANDATORY,则会加入该事物,并把newTransaction标志位设置为false;
3,如果当前事物不存在
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
// 如果没有事务定义信息则使用默认的事务管理器定义信息
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 获取事务
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 判断当前线程是否存在事务,判断依据为当前线程记录的连接不为空且连接中的transactionActive属性不为空
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// 当前线程已经存在事务
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// ********如果当前事物不存在,则向下走****************
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
// 事务超时设置验证
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// 如果当前线程不存在事务,但是PropagationBehavior却被声明为PROPAGATION_MANDATORY抛出异常
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,PROPAGATION_NESTED都需要新建事务
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
//没有当前事务的话,REQUIRED,REQUIRES_NEW,NESTED挂起的是空事务,然后创建一个新事务
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// 恢复挂起的事务
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
// 创建一个空的事务
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
如果当前事物不存在,则向下走:
1、 如果当前事物传播特性是MANDATORY,表示当前事物不存在,则抛出异常;
2、 如果当前事物传播特性是REQUIRED,REQUIRED_NEW,NESTED则都需要新建事务;
3、 如果当前事物传播特性是SUPPORT,NOT_SUPPORTED,NEVER表示不运行在事物中,则创建一个空的事物,transaction设置为null,newTransaction设置为true;
二,挂起事物
有些传播机制需要挂起当前的事务,比如NOT_SUPPORTED,REQUIRES_NEW首先会清除所有线程相关的同步状态,如果当前事务存在的话,就进行一些属性的清除,比如清空连接持有器,清空线程私有变量的同步状态,最后把当前事务清除的属性保存到一个SuspendedResourcesHolder里,以便于恢复的时候设置回去。
protected final SuspendedResourcesHolder suspend(@Nullable Object transaction) throws TransactionException {
// 判断当前的线程变量中有没有激活的事物,有需要清空线程变量
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
List<TransactionSynchronization> suspendedSynchronizations = doSuspendSynchronization();
try {
Object suspendedResources = null;
if (transaction != null) {
//挂起的资源,连接持有器
suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
}
// 获取当前事务名称
String name = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionName();
// 清空线程变量
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(null);
// 获取出只读事务的名称
boolean readOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly();
// 清空线程变量
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(false);
// 获取已存在事务的隔离级别
Integer isolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
// 清空隔离级别
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(null);
// 判断当前事务激活状态
boolean wasActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
// 清空标记
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(false);
// 把上诉从线程变量中获取出来的存在事务属性封装为挂起的事务属性返回出去
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(
suspendedResources, suspendedSynchronizations, name, readOnly, isolationLevel, wasActive);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// doSuspend failed - original transaction is still active...
doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations);
throw ex;
}
}
else if (transaction != null) {
// Transaction active but no synchronization active.
Object suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(suspendedResources);
}
else {
// Neither transaction nor synchronization active.
return null;
}
}
/**
* 实际挂起资源的方法
*/
@Override
protected Object doSuspend(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
// 清空连接持有器
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null);
// 解绑线程私有的资源
return TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(obtainDataSource());
}
/**
* 解绑数据源
*/
public static Object unbindResource(Object key) throws IllegalStateException {
// 获取数据源
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
// 获取解绑的连接持有器
Object value = doUnbindResource(actualKey);
return value;
}
private static Object doUnbindResource(Object actualKey) {
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
Object value = map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
value = null;
}
if (value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Removed value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] from thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
return value;
}
三,恢复事物
如果前面有事务被挂起,现在就要恢复,其实就是把一些属性设置回去:
protected final void resume(@Nullable Object transaction, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder resourcesHolder)
throws TransactionException {
// 设置属性和状态
if (resourcesHolder != null) {
Object suspendedResources = resourcesHolder.suspendedResources;
if (suspendedResources != null) {
doResume(transaction, suspendedResources);
}
List<TransactionSynchronization> suspendedSynchronizations = resourcesHolder.suspendedSynchronizations;
//如果有挂起同步器的话要设置线程私有变量的值为挂起事务的相关属性
if (suspendedSynchronizations != null) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(resourcesHolder.wasActive);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(resourcesHolder.isolationLevel);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(resourcesHolder.readOnly);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(resourcesHolder.name);
doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations);
}
}
}
/**
* 将挂起的事务连接持有器和数据源绑定,放入线程私有变量中
*/
@Override
protected void doResume(@Nullable Object transaction, Object suspendedResources) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), suspendedResources);
}
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");//每次在进行获取的时候都要根据obtainDataSource()返回的数据源来获取connectionHolder,现在经过设置会后,有了
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
// set ThreadLocal Map if none found
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap<>();
resources.set(map);
}
Object oldValue = map.put(actualKey, value);
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (oldValue instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) oldValue).isVoid()) {
oldValue = null;
}
if (oldValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already value [" + oldValue + "] for key [" +
actualKey + "] bound to thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Bound value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] to thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
}
四,执行目标方法
现在需要再次回到invokeWithinTransaction()方法中:
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取我们的事务属性源对象
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 通过事务属性源对象获取到当前方法的事务属性信息
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取我们配置的事务管理器对象
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 省略部分异常判断....
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
// 获取连接点的唯一标识 类名+方法名
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 声明式事务处理
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// 创建TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// 执行被增强方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
//清除事务信息,恢复线程私有的老的事务信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
//成功后提交,会进行资源储量,连接释放,恢复挂起事务等操作
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
// 省略编程式事物逻辑...
else{
}
// 省略部分代码...
return result;
}
}
}
前面我们已近通过createTransactionIfNecessary()方法获取到事物了,接下来需要调用invocation.proceedWithInvocation()来执行目标方法,invocation是一个回调函数,其是ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed()的回调,所以现在又回到了AOP拦截器的入口,此时会执行invokeJoinpoint()来执行目标方法:
/**
* 结账:传入哪个用户买了哪本书
* @param username
* @param id
*/
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void checkout(String username,int id){
// 减库存
bookDao.updateStock(id);
// 获取图书价格
// int price = bookDao.getPrice(id);
// 更新余额
// bookDao.updateBalance(username,price);
}
如果遇到异常,就会异常回滚。
五,异常回滚
如果支持回滚的话就进行回滚,否则就处理提交,提交里面如果TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly()=true的话也会进行回滚处理:
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
// 支持回滚则进行回滚
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
// 进行回滚
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// 否则进行提交,但是如果TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly(),仍然进行回滚
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
根据事物的状态来进行回滚:
/**
* 事务管理器根据事务状态来处理回滚
*/
@Override
public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
processRollback(defStatus, false);
}
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
try {
// 意外的回滚
boolean unexpectedRollback = unexpected;
try {
// 回滚完成前回调
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
// 有保存点回滚到保存点
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
}
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
}
// 当前状态是一个新事务
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
// 进行回滚
doRollback(status);
}
else {
// Participating in larger transaction
if (status.hasTransaction()) {
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
}
//设置连接要回滚标记,也就是全局回滚
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
}
else {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
}
}
}
else {
logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
}
// Unexpected rollback only matters here if we're asked to fail early
if (!isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = false;
}
}
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
throw ex;
}
// 回滚完成后回调
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
// Raise UnexpectedRollbackException if we had a global rollback-only marker
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
finally {
// 根据事务状态信息,完成后数据清除,和线程的私有资源解绑,重置连接自动提交,隔离级别,是否只读,释放连接,恢复挂起事务等
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
unexpected这个一般是false,除非是设置rollback-only=true,才是true,表示是全局的回滚标记。首先会进行回滚前回调,然后判断是否设置了保存点,比如NESTED会设置,要先回滚到保存点。如果状态是新的事务,那就进行回滚,如果不是新的,就设置一个回滚标记,内部是设置连接持有器回滚标记。然后回滚完成回调,根据事务状态信息,完成后数据清除,和线程的私有资源解绑,重置连接自动提交,隔离级别,是否只读,释放连接,恢复挂起事务等。
1、 如果有保存点,回滚到保存点;
2、 否则,如果当前是一个新事物(transaction!=null&&newTransaction==true),直接进行回滚;
3、 否则,设置全局回滚标记,如果既没有保存点,又不是新的事务,如果可以设置全局的回滚标记的话,就会设置;
4、 回滚后,根据事务状态信息,完成后数据清除,和线程的私有资源解绑,重置连接自动提交,隔离级别,是否只读,释放连接,恢复挂起事务等;
正回滚的处理方法,也就是获取JDBC连接,然后回滚:
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
try {
// jdbc的回滚
con.rollback();
}
}
回滚完成后,要进行清楚工作:
回滚后的处理工作,如果是新的事务同步状态的话,要把线程的同步状态清除了,如果是新事务的话,进行数据清除,线程的私有资源解绑,重置连接自动提交,隔离级别,是否只读,释放连接等。
如果有挂起的事务,还要把这个事务给恢复,其实就是把属性设置回去:
private void cleanupAfterCompletion(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
// 设置完成状态
status.setCompleted();
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
// 线程同步状态清除
TransactionSynchronizationManager.clear();
}
// 如果是新事务的话,进行数据清除,线程的私有资源解绑,重置连接自动提交,隔离级别,是否只读,释放连接等
if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
doCleanupAfterCompletion(status.getTransaction());
}
// 有挂起的事务要恢复
if (status.getSuspendedResources() != null) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Resuming suspended transaction after completion of inner transaction");
}
Object transaction = (status.hasTransaction() ? status.getTransaction() : null);
// 结束之前事务的挂起状态
resume(transaction, (SuspendedResourcesHolder) status.getSuspendedResources());
}
}
六,事物提交
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
调用事务管理器的提交方法:
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
// 如果在事务链中已经被标记回滚,那么不会尝试提交事务,直接回滚
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
// 不可预期的回滚
processRollback(defStatus, false);
return;
}
// 设置了全局回滚
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
// 可预期的回滚,可能会报异常
processRollback(defStatus, true);
return;
}
// 处理事务提交
processCommit(defStatus);
}
提交事务,就算没有异常,但是提交的时候也可能会回滚,因为有内层事务可能会标记回滚。
1、 如果在事务链中已经被标记回滚,那么不会尝试提交事务,直接回滚;
2、 如果设置了全局回滚,则进行全局回滚;
3、 如果没发生回滚,则提交事物;
事物的提交:
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = false;
// 预留
prepareForCommit(status);
// 添加的TransactionSynchronization中的对应方法的调用
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
// 提交完成前回调
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
// 有保存点
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
//是否有全局回滚标记
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// 如果存在保存点则清除保存点信息
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
//当前状态是新事务
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// 如果是独立的事务则直接提交
doCommit(status);
}
else if (isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
// 有全局回滚标记就报异常
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
}
else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
// 提交过程中出现异常则回滚
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
// 提交后回调
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
finally {
// 提交后清除线程私有同步状态
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
}
finally {
//根据条件,完成后数据清除,和线程的私有资源解绑,重置连接自动提交,隔离级别,是否只读,释放连接,恢复挂起事务等
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
如下步骤:
1、 先处理保存点,如果存在保存点则清除保存点信息;
2、 然后处理新事务(transaction!=null&&newTransaction==true),如果是独立的事务则直接提交;
3、 如果不是新事务不会真正提交,要等外层是新事务的才提交;
4、 提交过程中出现异常则回滚;
5、 根据条件,完成后数据清除,和线程的私有资源解绑,重置连接自动提交,隔离级别,是否只读,释放连接,恢复挂起事务等;
doCommit()获取JDBC的连接提交:
/**
* 获取JDBC的连接提交
*/
@Override
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
// JDBC连接提交
con.commit();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not commit JDBC transaction", ex);
}
}
七,总结
关于异常回滚:
1、 如果有保存点,回滚到保存点;
2、 否则,如果当前是一个新事物(transaction!=null&&newTransaction==true),直接进行回滚;
3、 否则,设置全局回滚标记,如果既没有保存点,又不是新的事务,如果可以设置全局的回滚标记的话,就会设置;
关于事物提交:
1、 如果在事务链中已经被标记回滚,那么不会尝试提交事务,直接回滚;
2、 如果设置了全局回滚,则进行全局回滚;
3、 如果是新事务(transaction!=null&&newTransaction==true),则直接提交;
4、 如果不是新事务不会提交,要等外层是新事务才提交;
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: