一,例子准备
切面类LogUtil.java
public class LogUtil {
private int start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//获取方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
//获取参数信息
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法开始执行:参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
return 100;
}
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法执行结束,结果是:"+result);
}
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception e){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法抛出异常:"+e.getMessage());
}
public static void logFinally(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法执行结束。。。。。over");
}
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("log---环绕通知start:"+signature.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数为:"+Arrays.asList(args));
result = pjp.proceed(args);
System.out.println("log---环绕通知stop"+signature.getName()+"方法执行结束");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("log---环绕异常通知:"+signature.getName()+"出现异常");
throw throwable;
}finally {
System.out.println("log---环绕返回通知:"+signature.getName()+"方法返回结果是:"+result);
}
return result;
}
}
MyCalculator.java
public class MyCalculator{
public Integer add(Integer i, Integer j) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Integer result = i+j;
return result;
}
public Integer sub(Integer i, Integer j) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Integer result = i-j;
return result;
}
public Integer mul(Integer i, Integer j) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Integer result = i*j;
return result;
}
public Integer div(Integer i, Integer j) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Integer result = i/j;
return result;
}
}
boboAopXmlTest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<bean id="logUtil" class="com.bobo.aop.xml.LogUtil"></bean>
<bean id="myCalculator" class="com.bobo.aop.xml.MyCalculator" ></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="logUtil">
<aop:pointcut id="myPoint" expression="execution( Integer com.bobo.aop.xml.MyCalculator.* (..))"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="myPoint"></aop:around>
<aop:before method="start" pointcut-ref="myPoint"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="logFinally" pointcut-ref="myPoint"></aop:after>
<aop:after-returning method="stop" pointcut-ref="myPoint" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="myPoint" throwing="e"></aop:after-throwing>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
MyTest.java
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("boboAopXmlText.xml");
}
}
二,创建BeanDefinition过程
在AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()的是十三个方法中,第二个方法 obtainFreshBeanFactory();
是负责DefaultListableBeanFactory的创建和XML文件的解析工作。
通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader的层层调用,最终会调到DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类的parseBeanDefinitions方法中:
1,DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#parseBeanDefinitions()
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
此方法会负责对配置文件的document树一行一行的解析,解析时分为默认标签(import,alias,bean,beans)的解析parseDefaultElement和自定义标签(除了以上四个默认标签,其余全是自定义标签)的解析parseCustomElement
其中logUtil和myCalculator这两个bean标签会通过parseDefaultElement解析为BeanDefinition放入BeanDefinitionMap中,这里比较简单,直接跳过了,重点看下面 aop标签的解析工作。
2,BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseCustomElement()
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
// 获取对应的命名空间
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
if (namespaceUri == null) {
return null;
}
// 根据命名空间找到对应的NamespaceHandlerspring
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
// 调用自定义的NamespaceHandler进行解析
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
获取对应的命名空间
通过Element获取当前标签对应的命名空间,此处namespaceUri是http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
根据命名空间找到对应的NamespaceHandler
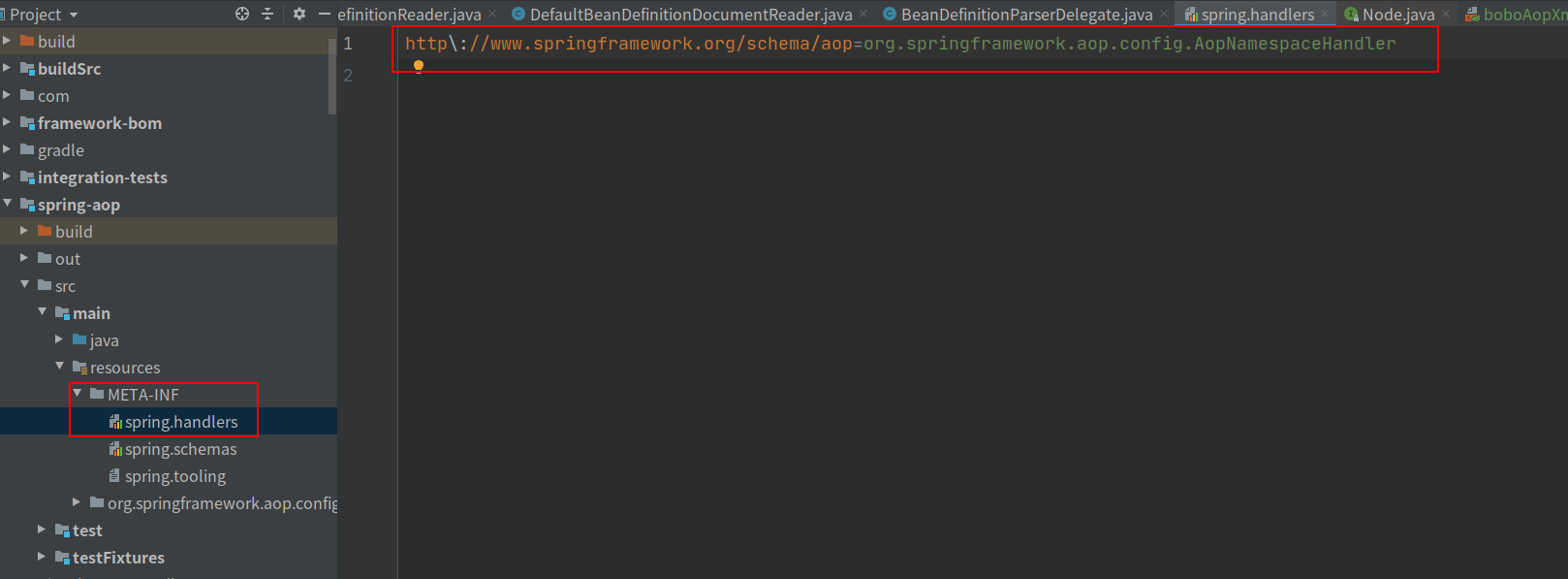
通过namespaceUri去 spring.handlers文件中找到对应的NamespaceHandler,这里获取到的是AopNamespaceHandler
调用对应的NamespaceHandler进行解析
public abstract class NamespaceHandlerSupport implements NamespaceHandler {
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 获取元素的解析器
BeanDefinitionParser parser = findParserForElement(element, parserContext);
return (parser != null ? parser.parse(element, parserContext) : null);
}
@Nullable
private BeanDefinitionParser findParserForElement(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 获取元素名称(此处的localName是config,因为标签为 aop:config)
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(element);
// 根据元素名称找到对应的解析器
BeanDefinitionParser parser = this.parsers.get(localName);
if (parser == null) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().fatal(
"Cannot locate BeanDefinitionParser for element [" + localName + "]", element);
}
return parser;
}
}
AopNamespaceHandler继承于NamespaceHandlerSupport,通过父类NamespaceHandlerSupport找到对应的BeanDefinitionParser此处对应的解析器为ConfigBeanDefinitionParser
3,ConfigBeanDefinitionParser#parse()
然后调用ConfigBeanDefinitionParser#parse()方法对aop:config标签中的子标签进行解析。
class ConfigBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef =
new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), parserContext.extractSource(element));
parserContext.pushContainingComponent(compositeDef);
// 注册自动代理模式创建器,AspectjAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
configureAutoProxyCreator(parserContext, element);
// 解析aop:config子节点下的aop:pointcut/aop:advice/aop:aspect
List<Element> childElts = DomUtils.getChildElements(element);
for (Element elt: childElts) {
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(elt);
if (POINTCUT.equals(localName)) {
parsePointcut(elt, parserContext);
}
else if (ADVISOR.equals(localName)) {
parseAdvisor(elt, parserContext);
}
else if (ASPECT.equals(localName)) {
parseAspect(elt, parserContext);
}
}
parserContext.popAndRegisterContainingComponent();
return null;
}
}
注册自动代理模式创建器AspectjAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
public abstract class AopNamespaceUtils {
public static void registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
// 注册名为org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator的beanDefinition,其中的class类为AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,其也会被注册到bean工厂中
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
// 如果指定proxy-target-class=true,则使用CGLIB代理,否则使用JDK代理
// 其实其为AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类的proxyTargetClass属性
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
// 注册到spring的bean工厂中,再次校验是否已注册
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}
}
上面逻辑为,把注册名为org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator的beanDefinition,其中的class类为AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,其也会被注册到bean工厂中。
判断使用JDK动态代理还是使用CGLib动态代理:
private static void useClassProxyingIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Element sourceElement) {
if (sourceElement != null) {
// 对于proxy-target-class属性的处理
/**
* SpringAOP部分使用JDK动态代理或者CGLIB来为目标创建代理,如果被代理的目标对象实现了至少一个接口,则会使用JDK动态代理。所有该目标类型实现的接口都将被
* 代理,若该目标对象没有实现任何接口,则创建一个cglib代理,
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass = Boolean.parseBoolean(sourceElement.getAttribute(PROXY_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE));
if (proxyTargetClass) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
// 对expose-proxy属性的处理
boolean exposeProxy = Boolean.parseBoolean(sourceElement.getAttribute(EXPOSE_PROXY_ATTRIBUTE));
if (exposeProxy) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
SpringAOP部分使用JDK动态代理或者CGLIB来为目标创建代理,如果被代理的目标对象实现了至少一个接口,则会使用JDK动态代理。所有该目标类型实现的接口都将被代理,若该目标对象没有实现任何接口,则创建一个cglib代理。
解析aop:config子节点下的aop:pointcut/aop:advice/aop:aspect
由于我们下面子节点只有一个aspect,所以调用parseAspect(elt, parserContext)方法,对aspect中的子结点进行解析:
4,ConfigBeanDefinitionParser#parseAspect()方法
对aspect中的子结点进行解析:
private void parseAspect(Element aspectElement, ParserContext parserContext) {
// <aop:aspect> id属性
String aspectId = aspectElement.getAttribute(ID);
// aop ref属性,必须配置。代表切面
String aspectName = aspectElement.getAttribute(REF);
try {
this.parseState.push(new AspectEntry(aspectId, aspectName));
List<BeanDefinition> beanDefinitions = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanReference> beanReferences = new ArrayList<>();
// 解析<aop:aspect>下的declare-parents节点
// 采用的是DeclareParentsAdvisor作为beanClass加载
List<Element> declareParents = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(aspectElement, DECLARE_PARENTS);
for (int i = METHOD_INDEX; i < declareParents.size(); i++) {
Element declareParentsElement = declareParents.get(i);
beanDefinitions.add(parseDeclareParents(declareParentsElement, parserContext));
}
// We have to parse "advice" and all the advice kinds in one loop, to get the
// ordering semantics right.
// 解析其下的advice节点
NodeList nodeList = aspectElement.getChildNodes();
boolean adviceFoundAlready = false;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
// 是否为advice:before/advice:after/advice:after-returning/advice:after-throwing/advice:around节点
if (isAdviceNode(node, parserContext)) {
// 校验aop:aspect必须有ref属性,否则无法对切入点进行观察操作
if (!adviceFoundAlready) {
adviceFoundAlready = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(aspectName)) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"<aspect> tag needs aspect bean reference via 'ref' attribute when declaring advices.",
aspectElement, this.parseState.snapshot());
return;
}
beanReferences.add(new RuntimeBeanReference(aspectName));
}
// 解析advice节点并注册到bean工厂中
AbstractBeanDefinition advisorDefinition = parseAdvice(
aspectName, i, aspectElement, (Element) node, parserContext, beanDefinitions, beanReferences);
beanDefinitions.add(advisorDefinition);
}
}
AspectComponentDefinition aspectComponentDefinition = createAspectComponentDefinition(
aspectElement, aspectId, beanDefinitions, beanReferences, parserContext);
parserContext.pushContainingComponent(aspectComponentDefinition);
// 解析aop:point-cut节点并注册到bean工厂
List<Element> pointcuts = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(aspectElement, POINTCUT);
for (Element pointcutElement : pointcuts) {
parsePointcut(pointcutElement, parserContext);
}
parserContext.popAndRegisterContainingComponent();
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
4.1,首先解析aop:aspect下的declare-parents节点
由于我们这里没有配置,所以这里为空,跳过
4.2,解析其下的advice节点
检查是否为advice:before/advice:after/advice:after-returning/advice:after-throwing/advice:around节点,如果是 则解析advice节点并注册到bean工厂中。
5,ConfigBeanDefinitionParser#parseAdvice()方法
解析advice节点并注册到bean工厂中:
private AbstractBeanDefinition parseAdvice(
String aspectName, int order, Element aspectElement, Element adviceElement, ParserContext parserContext,
List<BeanDefinition> beanDefinitions, List<BeanReference> beanReferences) {
try {
this.parseState.push(new AdviceEntry(parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(adviceElement)));
// create the method factory bean
// 解析advice节点中的"method"属性,并包装为MethodLocatingFactoryBean对象
RootBeanDefinition methodDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(MethodLocatingFactoryBean.class);
methodDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", aspectName);
methodDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("methodName", adviceElement.getAttribute("method"));
methodDefinition.setSynthetic(true);
// create instance factory definition
// 关联aspectName,包装为SimpleBeanFactoryAwareAspectInstanceFactory对象
RootBeanDefinition aspectFactoryDef =
new RootBeanDefinition(SimpleBeanFactoryAwareAspectInstanceFactory.class);
aspectFactoryDef.getPropertyValues().add("aspectBeanName", aspectName);
aspectFactoryDef.setSynthetic(true);
// register the pointcut
// 涉及point-cut属性的解析,并结合上述的两个bean最终包装为AbstractAspectJAdvice通知对象
AbstractBeanDefinition adviceDef = createAdviceDefinition(
adviceElement, parserContext, aspectName, order, methodDefinition, aspectFactoryDef,
beanDefinitions, beanReferences);
// configure the advisor
// 最终包装为AspectJPointcutAdvisor对象
RootBeanDefinition advisorDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(AspectJPointcutAdvisor.class);
advisorDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(adviceElement));
advisorDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(adviceDef);
if (aspectElement.hasAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY)) {
advisorDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ORDER_PROPERTY, aspectElement.getAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY));
}
// register the final advisor
parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(advisorDefinition);
return advisorDefinition;
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
private AbstractBeanDefinition createAdviceDefinition(
Element adviceElement, ParserContext parserContext, String aspectName, int order,
RootBeanDefinition methodDef, RootBeanDefinition aspectFactoryDef,
List<BeanDefinition> beanDefinitions, List<BeanReference> beanReferences) {
// 首先根据adviceElement节点分析出是什么类型的Advice
RootBeanDefinition adviceDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(getAdviceClass(adviceElement, parserContext));
adviceDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(adviceElement));
// 设置aspectName属性和declarationOrder属性
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(ASPECT_NAME_PROPERTY, aspectName);
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(DECLARATION_ORDER_PROPERTY, order);
// 解析节点是否含有returning/throwing/arg-names,有则设置
if (adviceElement.hasAttribute(RETURNING)) {
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
RETURNING_PROPERTY, adviceElement.getAttribute(RETURNING));
}
if (adviceElement.hasAttribute(THROWING)) {
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
THROWING_PROPERTY, adviceElement.getAttribute(THROWING));
}
if (adviceElement.hasAttribute(ARG_NAMES)) {
adviceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ARG_NAMES_PROPERTY, adviceElement.getAttribute(ARG_NAMES));
}
// 设置构造函数的入参变量
// Method/AspectJExpressionPointcut/AspectInstanceFactory三个入参
ConstructorArgumentValues cav = adviceDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(METHOD_INDEX, methodDef);
// 解析point-cut属性
Object pointcut = parsePointcutProperty(adviceElement, parserContext);
if (pointcut instanceof BeanDefinition) {
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(POINTCUT_INDEX, pointcut);
beanDefinitions.add((BeanDefinition) pointcut);
}
else if (pointcut instanceof String) {
RuntimeBeanReference pointcutRef = new RuntimeBeanReference((String) pointcut);
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(POINTCUT_INDEX, pointcutRef);
beanReferences.add(pointcutRef);
}
cav.addIndexedArgumentValue(ASPECT_INSTANCE_FACTORY_INDEX, aspectFactoryDef);
return adviceDefinition;
}
把上述代码执行完,按照如下图包裹完成:
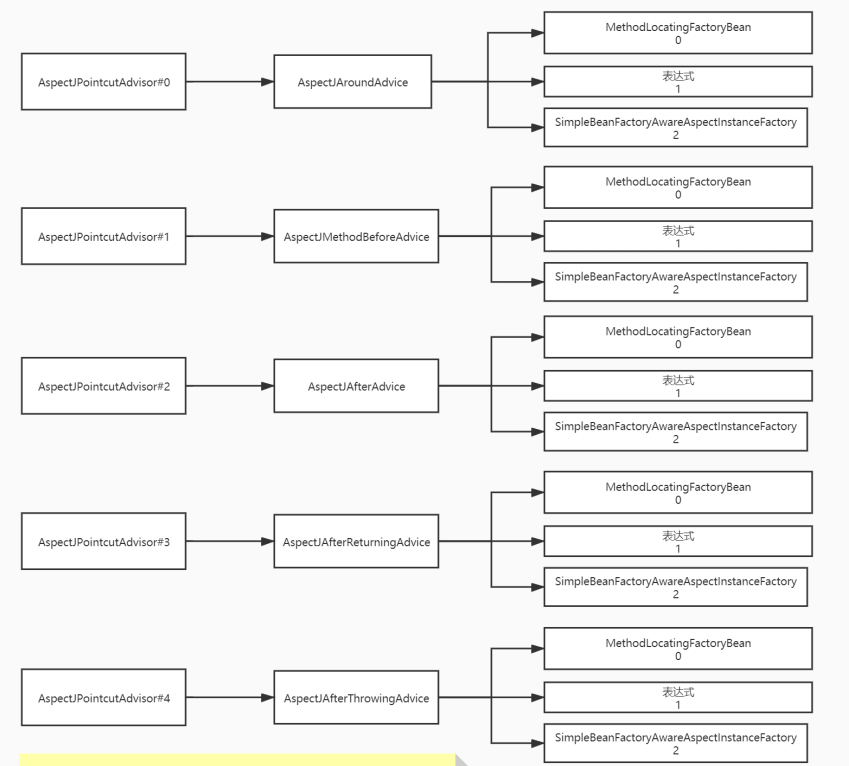
其中MethodLocatingFactoryBean中包含了,配置文件中method的name值:
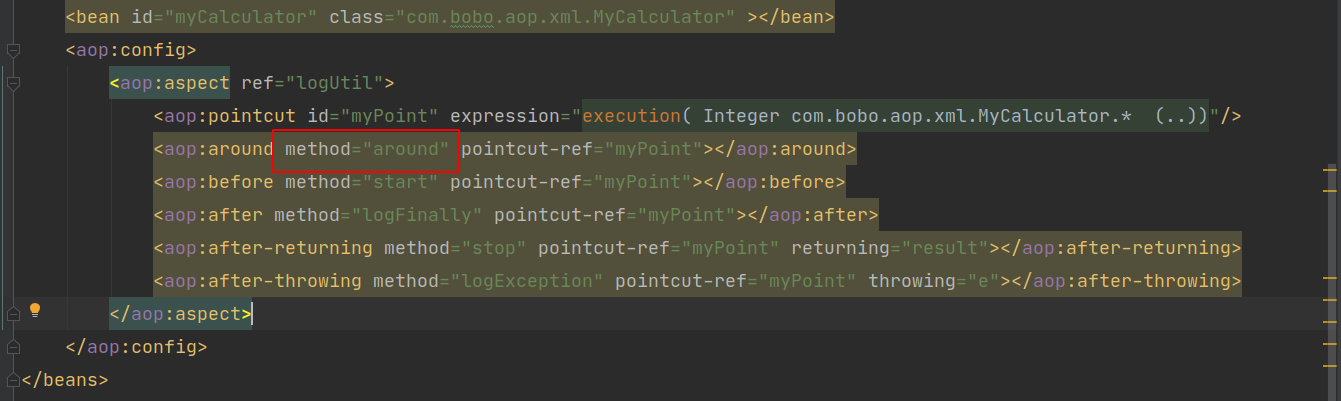
表达式中包含了pointCut
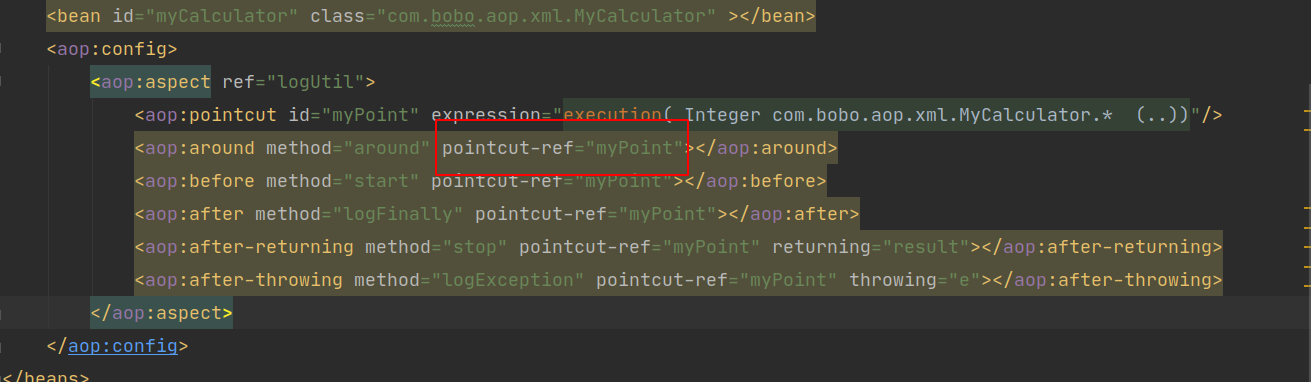
SimpleBeanFactoryAwareAspectInstanceFactory中包含了切面名字:
6,如上解析完成
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<bean id="logUtil" class="com.bobo.aop.xml.LogUtil"></bean>
<bean id="myCalculator" class="com.bobo.aop.xml.MyCalculator" ></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="logUtil">
<aop:pointcut id="myPoint" expression="execution( Integer com.bobo.aop.xml.MyCalculator.* (..))"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="myPoint"></aop:around>
<aop:before method="start" pointcut-ref="myPoint"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="logFinally" pointcut-ref="myPoint"></aop:after>
<aop:after-returning method="stop" pointcut-ref="myPoint" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="myPoint" throwing="e"></aop:after-throwing>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
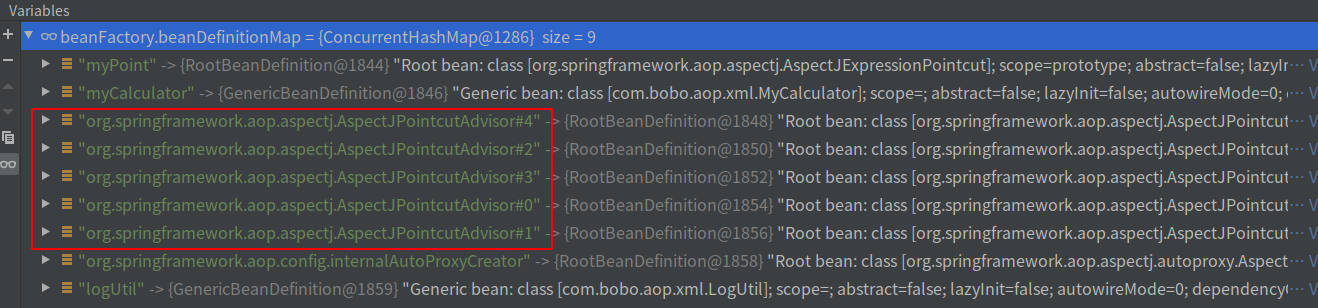
最终会放入BeanDefinitionMap中如下9个:
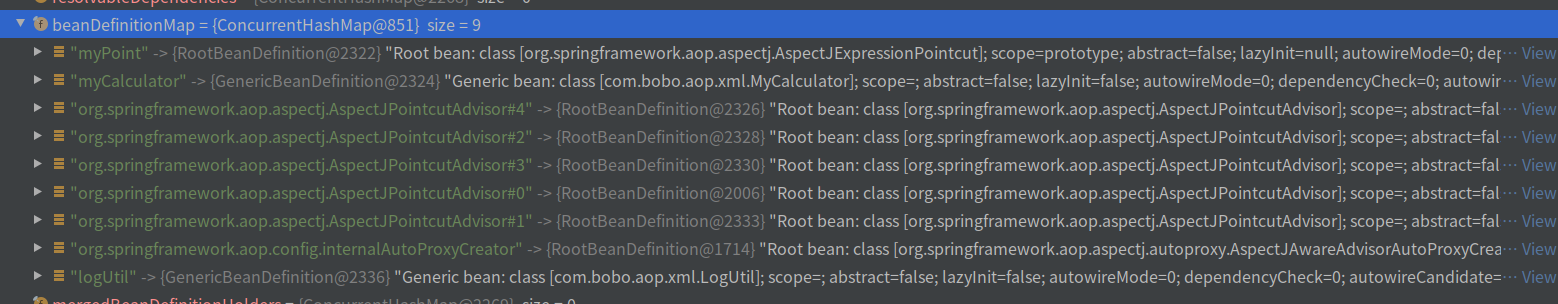
其中logUtil和myCalculator就不用再说了,普通的bean类。
6.1,myPoint
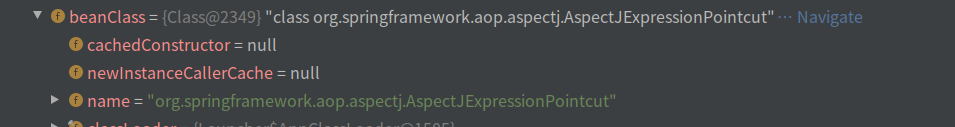
其中myPoint被解析成AspectJExpressionPointcut对象
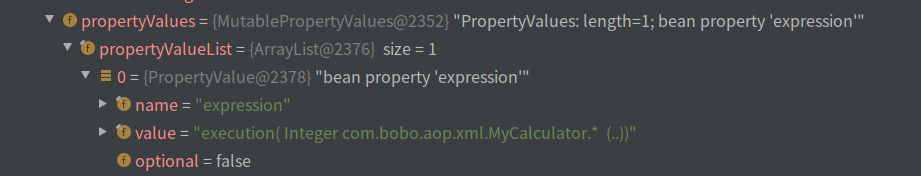
其中propertyValue中保存了我们写的表达式
6.2,around
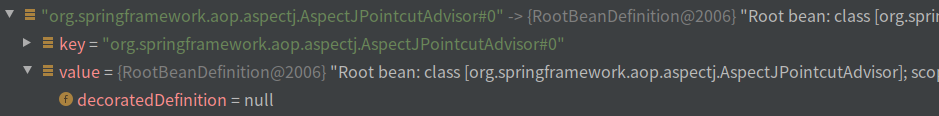
在constructorArgumentValues中保存了AspectJAroundAdvice类
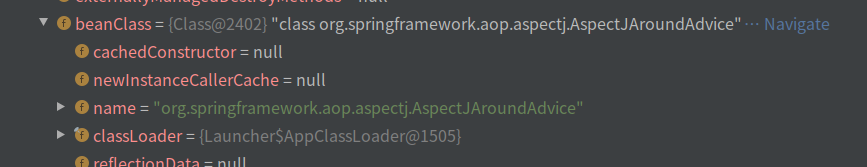
在AspectJAroundAdvice类的constructorArgumentValues参数中
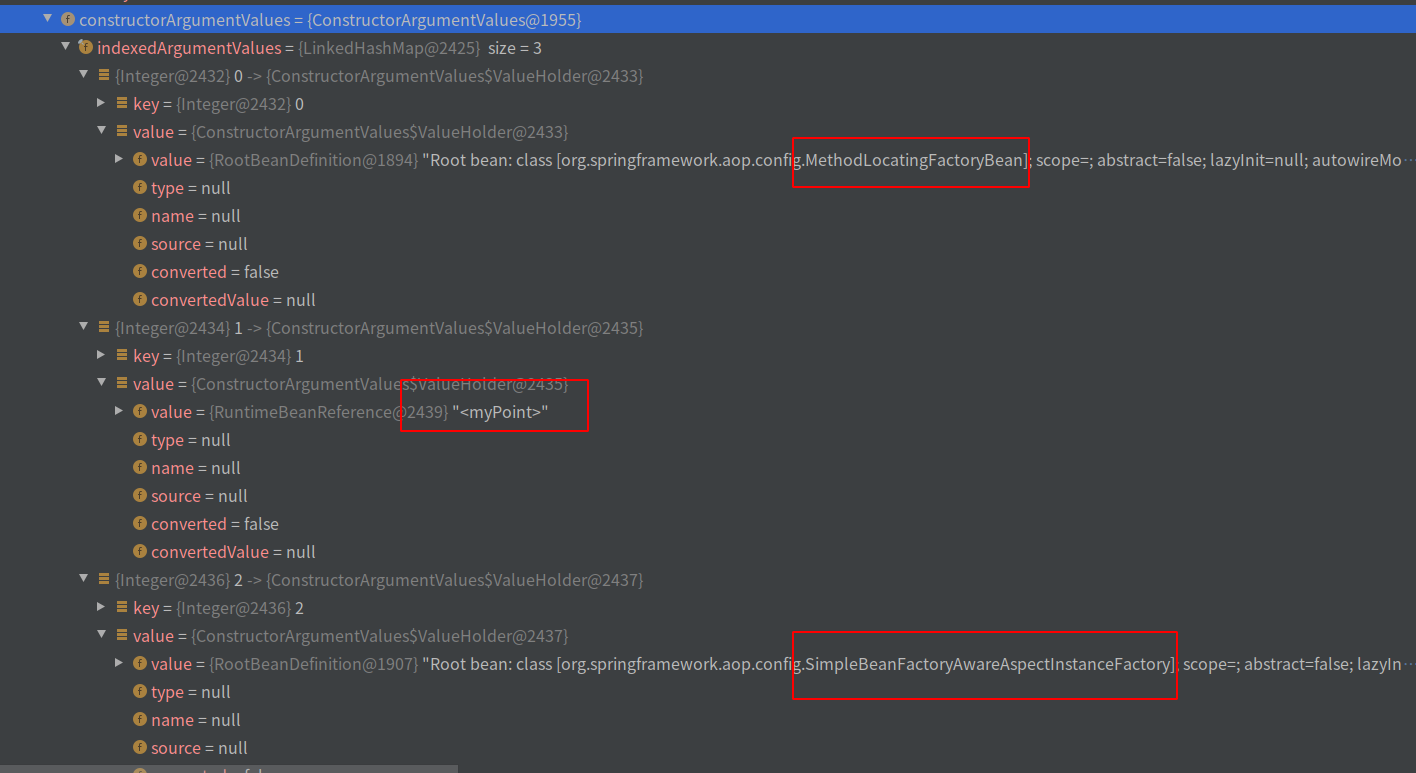
保存了MethodLocatingFactoryBean,myPoint表达式,SimpleBeanFactoryAwareAspectInstanceFactory
三,准备Advisor对象
在ferfesh()方法中beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();来实例化对象时,会遍历当前beanDefinitionNames集合,一个一个来实例化。
当实例化第一个BeanDefinition对象的过程中,会在getBean()–>doGetBean()—>createBean()方法中:
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// 省略部分代码...
try {
// 给BeanPostProcessors一个机会来返回代理来替代真正的实例,应用实例化前的前置处理器,用户自定义动态代理的方式,针对于当前的被代理类需要经过标准的代理流程来创建对象
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
try {
// 实际创建bean的调用
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
// 省略部分代码...
}
resolveBeforeInstantiation()方法,给BeanPostProcessors一个机会来返回代理来替代真正的实例。执行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation()方法:
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
用来执行InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor类型的处理器postProcessBeforeInstantiation()方法,这里主要关注AbstractAutoProxyCreator类:
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
//查缓存,是否有处理过了,不管是不是需要通知增强的,只要处理过了就会放里面
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
// 要跳过的直接设置FALSE
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
}
}
其中isInfrastructureClass()方法:
protected boolean isInfrastructureClass(Class<?> beanClass) {
boolean retVal = Advice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
if (retVal && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Did not attempt to auto-proxy infrastructure class [" + beanClass.getName() + "]");
}
return retVal;
}
判断bean的类型是不是内部的类型,比如Advice,Pointcut,Advisor,AopInfrastructureBean这些是跟AOP相关的,所以不应该被处理,直接就返回 true,然后加入advisedBeans里面,返回null不再往下走这里的流程,而是向下走正常实例化当前Bean的流程。
这里我们当前的bean是要实例化的第一个bean,是logUtil,所以如果当前bean不是以上Advice,Pointcut,Advisor,AopInfrastructureBean的bean的话,会向下走到下一个方法shouldSkip();
public class AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator extends AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator {
/**
* 找出Aspect切面和解析通知器的方法,通知器Advisor里面有通知Advice实例
*/
@Override
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 找出Aspect切面和解析通知器的方法
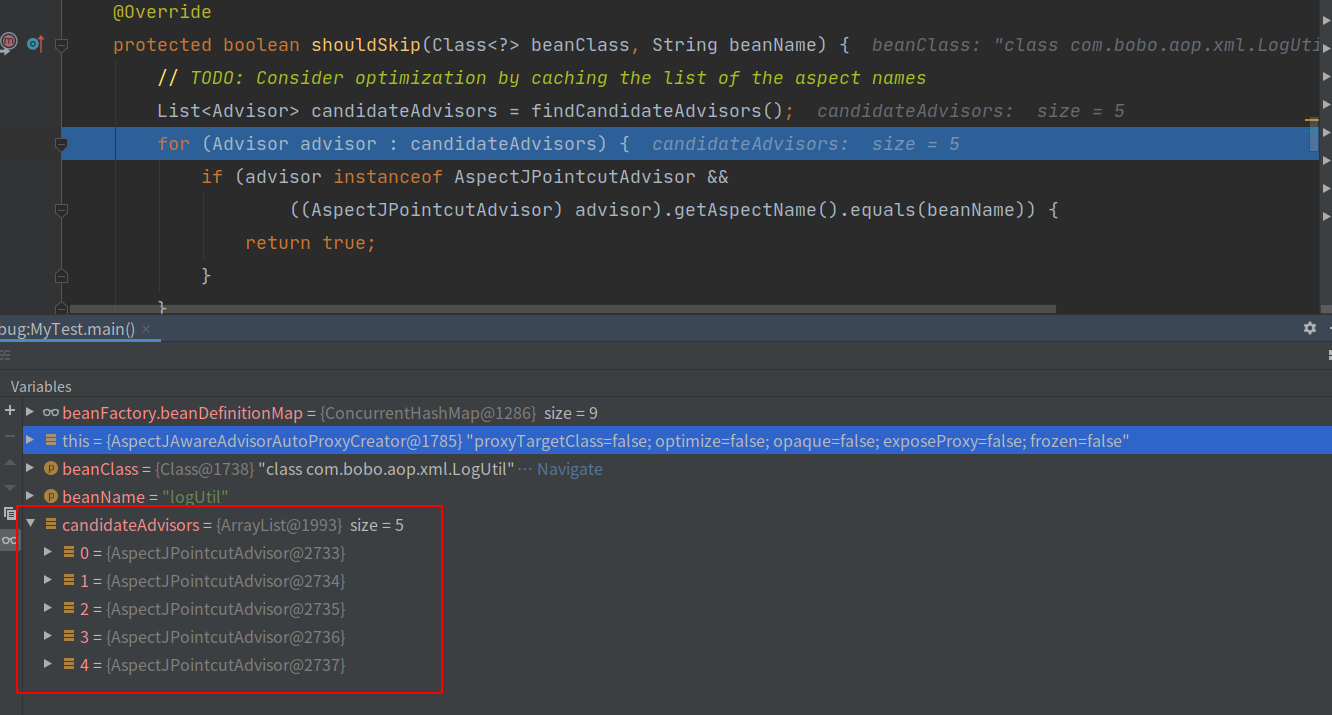
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {
if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&
((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {
return true;
}
}
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);
}
}
这里的findCandidateAdvisors()方法目的是找出所有的Advisor类,并且实例化:
/**
* 寻找所有Advisor.class的bean名字,如果存在就放入缓存,并进行创建,然后返回
*/
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) {
// 获取当前BeanFactory中所有实现了Advisor接口的bean的名称
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
// 对获取到的实现Advisor接口的bean的名称进行遍历
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环所有的beanName,找出对应的增强方法
for (String name : advisorNames) {
// isEligibleBean()是提供的一个hook方法,用于子类对Advisor进行过滤,这里默认返回值都是true
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
try {
// 将当前bean添加到结果中
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
}
}
}
return advisors;
}
这里会遍历当前BeanDefinitionMap中所有的Advisor类来一个个地实例化:
目前我们例子中有AspectJPointcutAdvisor#0-4五个Advisor类,实例化这五个Advisor比较复杂:
- 创建AspectJPointcutAdvisor#0-4,首先要使用其带参的构造方法进行对象的创建,但是想使用带参数的构造方法必须要把参数对象准备好,因此要准备创建内置包含的对象AspectJAroundAdvice
2、 创建AspectJAroundAdvice,也需要使用带参数的构造方法进行创建,也需要提前准备好具体的参数对象,包含三个参数MethodLocatingFactoryBean,AspectJExpressionPointcut,SimpleBeanFactoryAwareAspectInstanceFactory;
3、 分别创建上述三个对象,上述三个对象的创建过程是调用无参的构造方法;
4、 创建上述所有的都想都会走Spring实例化过程getBean()—>doGetBean()—>createBean()—>doCreateBean()…等流程,所以比较复杂;
上述流程走完,五个Advisor对象都已经实例化完成:
四,实例化AOP对象
当LogUtil类实例化完,该实例化MyCalculator类了,注意,MyCalculator类是我们实际要执行的类,是需要创建代理的,所以这里我们一起来分析一下AOP代理对象的创建:
创建代理对象是在实例化方法的getBean()--->doGetBean()--->createBean()--->doCreateBean()--->initializeBean()方法的,执行后置处理器的applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()方法中:
/**
* 初始化给定的bean实例,应用工厂回调以及init方法和BeanPostProcessors
*/
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// Aware接口处理器,调用BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、beanFactoryAware
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
//如果mdb不为null || mbd不是"synthetic"。一般是指只有AOP相关的prointCut配置或者Advice配置才会将 synthetic设置为true
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 将BeanPostProcessors前置处理器方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//调用初始化方法,先调用bean的InitializingBean接口方法,后调用bean的自定义初始化方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
//如果mbd为null || mbd不是"synthetic"
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 调用BeanPostProcessors后置处理器方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
//返回包装后的Bean
return wrappedBean;
}
代理对象的创建是在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的后置处理器方法postProcessAfterInitialization()中完成的。
/**
* ProxyProcessorSupport的重要子类。SpringAOP中的核心类。
* 实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryAware接口。
* 自动创建代理对象的类。我们在使用AOP的时候基本上都是用的这个类来进程Bean的拦截,创建代理对象。
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
/**
* 此处是真正创建aop代理的地方,在实例化之后,初始化之后就行处理
* 首先查看是否在earlyProxyReferences里存在,如果有就说明处理过了,不存在就考虑是否要包装,也就是代理
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
// 获取当前bean的key:如果beanName不为空,则以beanName为key,如果为FactoryBean类型,
// 前面还会添加&符号,如果beanName为空,则以当前bean对应的class为key
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 判断当前bean是否正在被代理,如果正在被代理则不进行封装
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
// 如果它需要被代理,则需要封装指定的bean
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
}
真正的实现是在wrapIfNecessary()方法中完成的:
/**
* 先判断是否已经处理过,是否需要跳过,跳过的话直接就放进advisedBeans里,表示不进行代理,
* 如果这个bean处理过了,获取通知拦截器,然后开始进行代理
*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 省略部分代码...
// 获取当前bean的Advices和Advisors
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 对当前bean的代理状态进行缓存
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
// 对当前bean的代理状态进行缓存
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 根据获取到的Advices和Advisors为当前bean生成代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
// 缓存生成的代理bean的类型,并且返回生成的代理bean
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
这里分为两步:
1、 找到所有符合创建当前代理Bean的Advisors对象;
2、 根据获取到的Advisors为当前bean生成代理对象;
1,找到所有符合创建当前代理Bean的Advisors对象
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 第一步,拿到我们前面准备好的Advisor对象集合
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 第二步,对获取到的所有Advisor进行判断,看其切面定义是否可以应用到当前bean,从而得到最终需要应用的Advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 提供的hook方法,用于对目标Advisor进行扩展
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
// 对需要代理的Advisor按照一定的规则进行排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
第一步:不用多说了,就是从缓存中拿到我们前面准备好的所有Advisor对象集合。
第二步:对获取到的所有Advisor进行判断,看其切面定义是否可以应用到当前bean,从而得到最终需要应用的Advisor。
public abstract class AopUtils {
/**
* 遍历每一个advisor,然后判断是否可以应用到目标类clazz上,可以的话就加入候选列表
*/
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
// 省略部分代码...
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 省略部分代码...
// 真正的判断增强器是否合适当前类型
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
// 这里是直接调用的ClassFilter的matches方法
// 如果当前advisor并没有对当前Bean(MyCalculator)类增强的话,直接返回不再向下判断
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
// 这里从Advisor中获取Pointcut的实现类 这里是AspectJExpressionPointcut
// 上面已经对类进行筛选过了,这里是对方法进行筛选
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
}
我们进入到对方法进行匹配的canApply()方法:
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
// 省略部分代码...
// 创建一个集合用于保存targetClass的class对象
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 判断当前class是不是代理的class对象
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
// 加入到集合中去
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
// 获取到targetClass所实现的接口的class对象,然后加入到集合中
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
// 循环所有的class对象
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
// 通过class获取到所有的方法
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
// 循环我们的方法
for (Method method : methods) {
// 只要有一个方法能匹配到就返回true
// 这里就会有一个问题:因为在一个目标中可能会有多个方法存在,有的方法是满足这个切点的匹配规则的
// 但是也可能有一些方法是不匹配切点规则的,这里检测的是只有一个Method满足切点规则就返回true了
// 所以在运行时进行方法拦截的时候还会有一次运行时的方法切点规则匹配
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
// 通过方法匹配器进行匹配
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
- 首先获取当前Bean的class对象
- 拿到class对象中的所有方法,循环遍历所有方法,只要有一个和Advisor中的方法匹配就返回true,证明此Advisor符合当前Bean创建代理。
只要有一个方法能匹配到就返回true,这里就会有一个问题:因为在一个目标中可能会有多个方法存在,有的方法是满足这个切点的匹配规则的,但是也可能有一些方法是不匹配切点规则的,这里检测的是只有一个Method满足切点规则就返回true了,所以在运行时进行方法拦截的时候还会有一次运行时的方法切点规则匹配。
通过上面匹配规则,找到所有符合创建当前代理Bean的Advisors对象,运行完成后,我们发现我们写的这五个都符合,因为用的都是同一个pointCut:
<aop:pointcut id="myPoint" expression="execution( Integer com.bobo.aop.xml.MyCalculator.* (..))"/>
2,创建代理对象
根据获取到的Advices和Advisors为当前bean生成代理对象:
/**
* 进行代理工厂的创建,然后判断是否需要设置proxyTargetClass,以便于后面决定是不是要进行jdk动态代理还是cglib的动态代理
* 然后把通知器advisors包装下,加入到代理工厂,获取代理对象
*/
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
// 给bean定义设置暴露属性
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 创建代理工厂
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// 获取当前类中相关属性
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// 决定对于给定的bean是否应该使用targetClass而不是他的接口代理,检查proxyTargetClass设置以及preserverTargetClass属性
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
// 判断是 使用jdk动态代理 还是cglib代理
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
// 添加代理接口
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 构建增强器
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
// 设置到要代理的类
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
// 定制代理
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
// 控制代理工程被配置之后,是否还允许修改通知,默认值是false
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 真正创建代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
进行一些列准备之后,进入到实际创建代理对象的方法:
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {
/**
* 获取cglib的代理对象
* @param classLoader the class loader to create the proxy with
* (or {@code null} for the low-level proxy facility's default)
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
// 从advised中获取ioc容器中配置的target对象
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
// 创建及配置Enhancer
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
// 配置超类,代理类实现的接口,回调方法等
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
// 获取callbacks
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// 通过 Enhancer 生成代理对象,并设置回调
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
}
}
用Enhancer创建代理类的原理,我们后面有事件会分析!
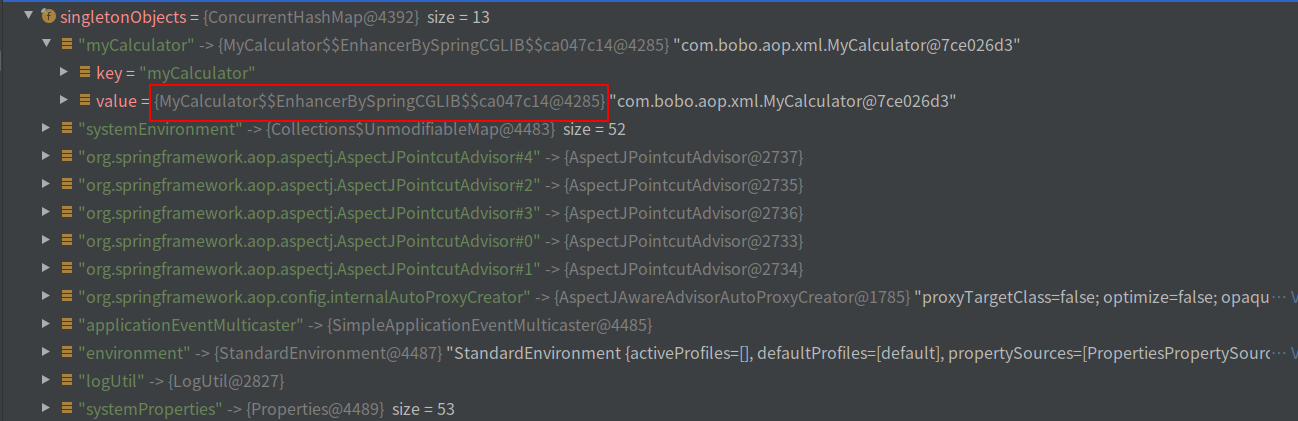
通过上面步骤,代理对象已经创建完成:
五,总结
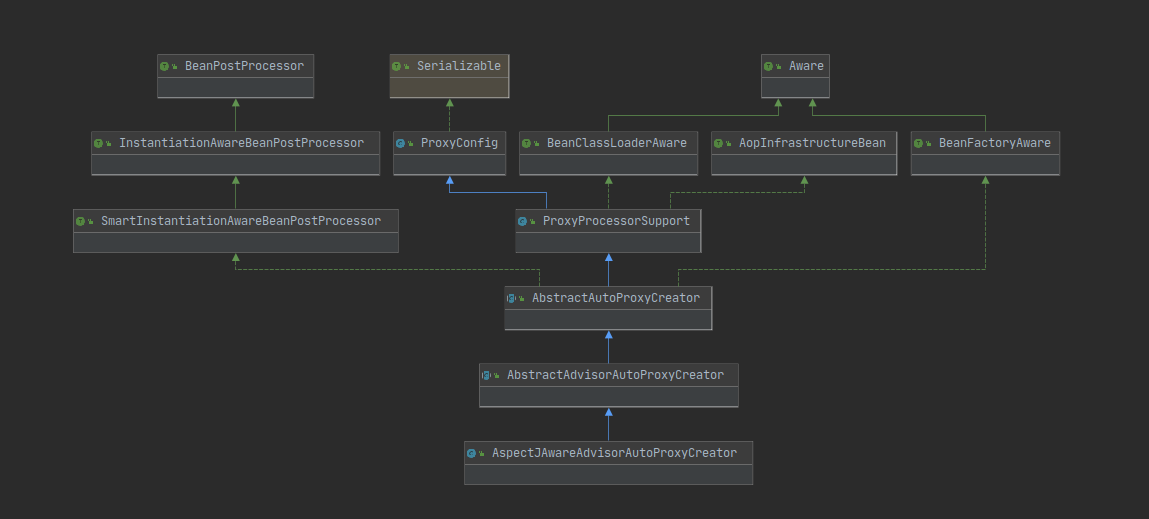
- 在解析aop:config标签之前会先注入AspectjAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类
- AspectjAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator继承于AbstractAutoProxyCreator类,其中AbstractAutoProxyCreator类实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor\接口,所以是BeanPostProcessor(BPP)。
- 在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessBeforeInstantiation()方法中完成所有Advisor的实例化。
- 在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法中完成AOP代理类的创建
版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: