前言
我们知道servlet程序需要使用servlet容器运行,那么DispatcherServlet是如何在spring boot内嵌tomcat容器进行初始化的呢?
1. 启动tomcat
首先点击启动类,启动spring boot 程序,然后进入了ServletWebServerApplicationContext类的createWebServer方法,开始创建一个web服务器。
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
// 1. 获取容器工厂
ServletWebServerFactory factory = this.getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
// 2. 使用工厂获取容器
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{
this.getSelfInitializer()});
createWebServer.end();
this.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown", new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
this.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop", new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
this.getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", var5);
}
}
// 3. 初始化PropertySources配置
this.initPropertySources();
}
可以看到这段代码走完后,打印了tomcat启动相关日志。
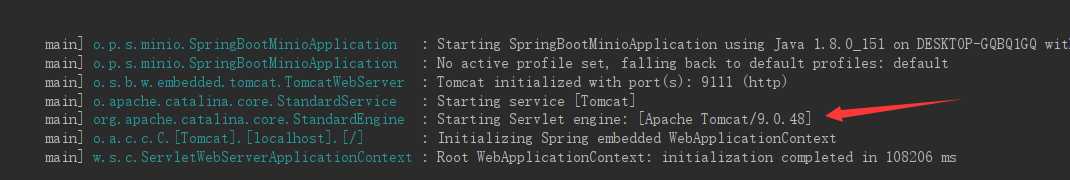
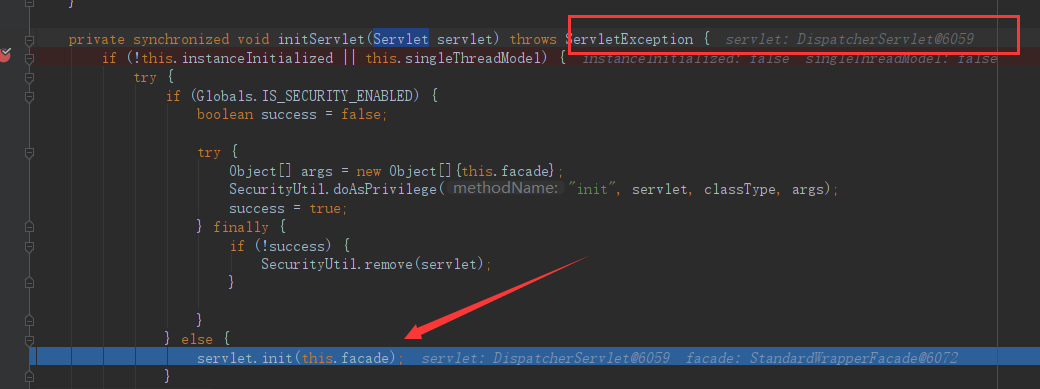
之后进入StandardWrapper的initServlet方法,开始初始化我们的Servlet。该方法的参数Servlet,就是DispatcherServlet,是由springboot自动配置功能事先注入到了IOC容器中的。
initServlet最终调用DispatcherServlet的init方法,并将当ServletConfig传递了过去。
2. 初始化WebApplicationContext
在上面最后的init方法中,DispatcherServlet调用的是父类HttpServletBean的init()方法,该方法最后又调用了initServletBean() 方法。
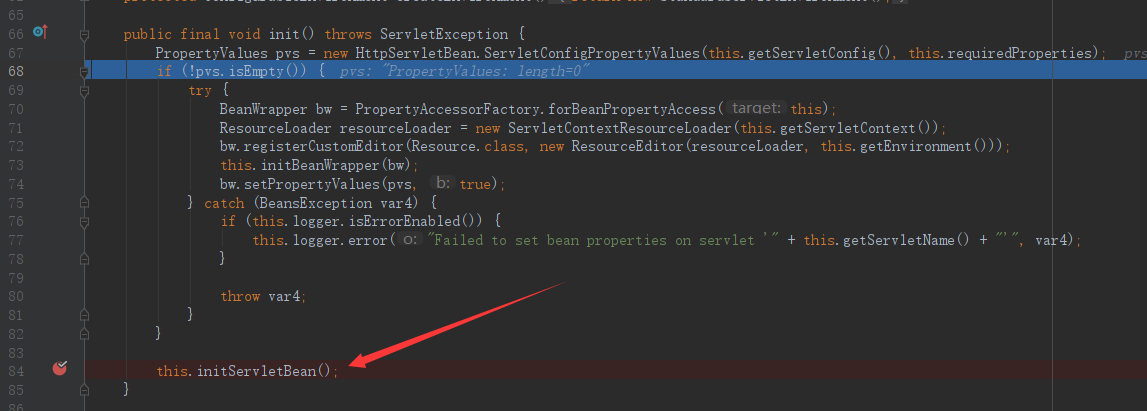
initServletBean() 方法调用的是父类FrameworkServlet。
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
// 1. 打印日志 Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet'
this.getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
// 2. 打印日志 Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
this.logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 3. 初始化WebApplicationContext
this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext();
// 4. 初始化FrameworkServlet
this.initFrameworkServlet();
} catch (RuntimeException | ServletException var4) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var4);
throw var4;
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ? "shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" : "masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
this.logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails + "': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
在initServletBean() 方法中,首先会调用FrameworkServlet类的initWebApplicationContext()方法,初始化WebApplicationContext。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 1. 查询WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 2. 已创建WebApplicationContext
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 3.再查询一遍,看其父类的是否已经注册了对应的context.
if (wac == null) {
wac = this.findWebApplicationContext();
}
// 4. 实在没找到,创建一个
if (wac == null) {
wac = this.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
// 5. 刷新容器
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized(this.onRefreshMonitor) {
this.onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = this.getServletContextAttributeName();
this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
如果不存在,就会创建一个WebApplicationContext 。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 1. 通过反射创建 IOC 容器对象
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// 2. 设置父容器
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
最后看下我们创建的WebApplicationContext。
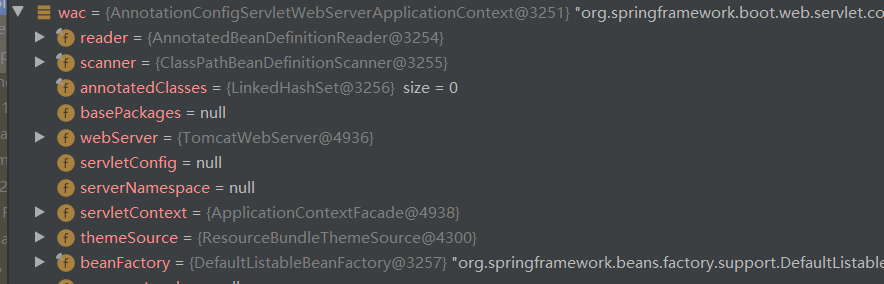
3. 刷新容器
FrameworkServlet中的initWebApplicationContext创建WebApplicationContext后,刷新容器,调用onRefresh(wac),此方法在DispatcherServlet中进行了重写,调用了initStrategies(context)方法,初始化策略,即初始化DispatcherServlet的各个组件。
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
最终回到FrameworkServlet的initServletBean方法,打印日志。
控制台日志如下,Completed initialization表示我们DispatcherServlet初始化完成了。

版权声明:本文不是「本站」原创文章,版权归原作者所有 | 原文地址: